AQI Based Graded Response Action Plan for Delhi Explained
Air pollution has become a consistent environmental challenge in Delhi in recent years. An air quality based graded response system is now being put in place which could increase your parking rates and close down schools during peak pollution days. What is important to understand is if it will actually help bring down Delhi’s air pollution and what role can citizens play in helping the Government fight this life threatening menace. Here’s a quick understanding of this AQI based graded response system.
The Hon’ble Supreme Court of India directed the framing and submission of graded response action plan for various categories of National Air Quality Index (AQI) on 10 November, 2016. An AQI is a number which considers the health impact of individual air pollutant (e.g. particulate matter, sulphur dioxide etc.), rates them according to how much threat they can cause to us and how much time they are higher than the prescribed standard in the air around us.
The end product is one number (which is arrived after combining and including all the different air pollutants that are measured) and is therefore easier to communicate to the general public. Since different countries have different pollution standards, an AQI is specific to each country.
The National Air Quality Index in India is calculated after measuring and considering the following air pollutants: Particulate Matter 10 (particle size 10 μm or less), Particulate Matter 2.5 (particle size of 2.5 μm or less), nitrogen dioxide, ozone, carbon monoxide, sulphur dioxide, ammonia and Lead. The AQI varies from 0 to 500 and is illustrated in the below table.
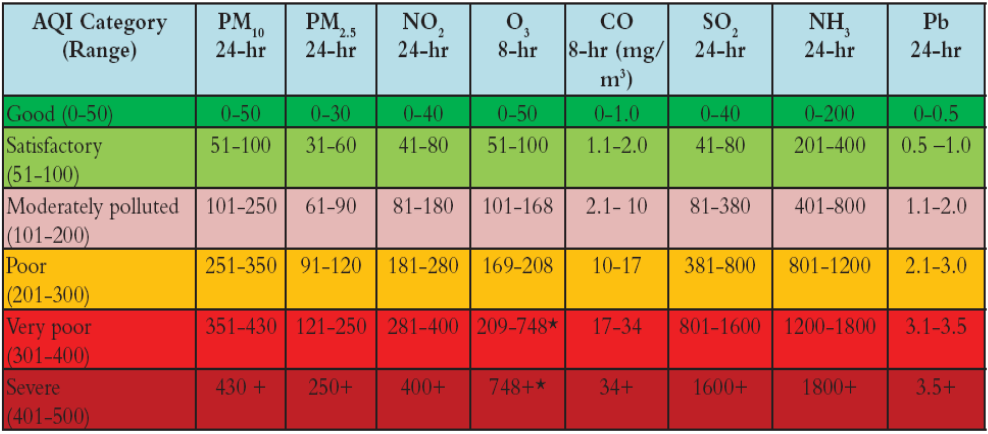
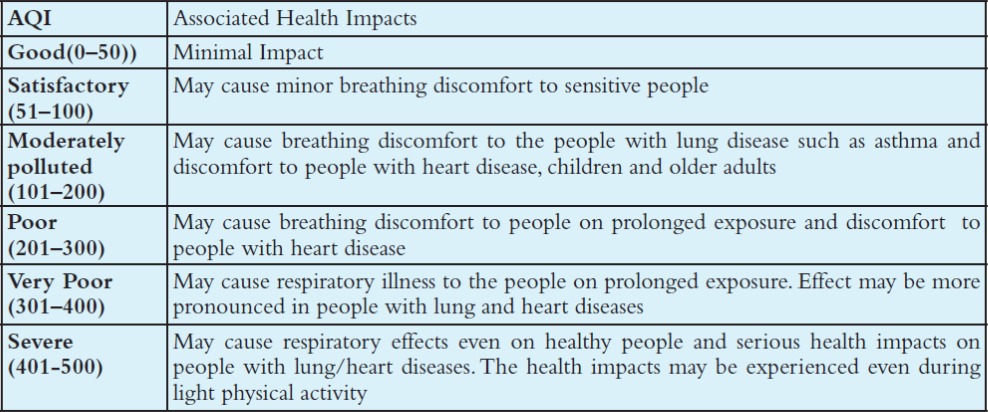
The graded measures/response strategy made by the Government has kept the AQI in mind and has been framed according to the AQI categories. It has also taken into account the broad health advisory for each level of AQI. The AQI based health advisory is as follows:
Analysis of the past air quality trend in Delhi shows that Severe and Very Poor air quality can be expected throughout the winter months of November to February and largely Poor category air quality can be expected during the summer months, from March to May. Consequently, Central Government has now assigned the task of implementation of the Graded Response Action Plan to the Environment Pollution Control Authority (EPCA) which was first established in 1998.
The EPCA had played a key role in the implementation of CNG in Delhi. The EPCA now needs to monitor a Control Room in the Delhi Pollution Control Committee (DPCC) and an NCR based Task Force for ensuring the implementation of this Supreme Court order on Graded Response to Air Pollution crisis in Delhi.
The Graded Response is based entirely on the AQI value, and mainly on the Particulate Matter (PM) pollution in Delhi. PM 10 and PM 2.5 are the key parameters based on which the Government has assigned response action as well as the agency responsible for implementing the response. The Graded Response strategy is tabulated below.
1. Severe+ or Emergency
- PM 2.5 levels cross 300 μg/cu.m Or
- PM 10 levels cross 500 μg/cu.m (5 times above the standard) and persist for 48 hours or more
| Action to be Taken | Agency Responsible/ Implementing Agency |
| Stop entry of truck traffic into Delhi (except essential commodities) | Municipal Corporations and Traffic Police of Delhi and NCR Towns |
| Stop construction activities | DPCC/ Municipal Corporations of Delhi and NCR Towns |
| Introduce odd and even scheme for private vehicles based on license plate numbers and minimize exemptions | Secretary cum Commissioner of Transport Department, NCT of Delhi, and Transport Commissioners of NCR Towns |
| Task Force to take decision on any additional steps including shutting of Schools |
2. Severe
- PM 2.5 levels are above 250 μg/cu.m Or
- PM 10 levels are above 430 μg/cu.m
| Action to be Taken | Agency Responsible/ Implementing Agency |
| Close brick kilns, Hot Mix plants, Stone Crushers | Chairpersons of DPCC and State Pollution Control Boards of Haryana, Rajasthan and Uttar Pradesh. Superintendent of Police and Deputy Commissioner of respective districts. |
| Shut down Badarpur power plant and maximize generation of power from existing natural gas based plants to reduce operation of coal based power plants in the NCR. | Chairpersons of DPCC and State Pollution Control Boards of Haryana, Rajasthan, and Uttar Pradesh |
| Intensify public transport services. Introduce differential rates to encourage off-peak travel. | Secretary cum Commissioner of Transport Department, NCT of Delhi and Transport Commissioners of NCR towns. Chairperson, DMRC and Chairpersons, State Transport Corporations |
| Increase frequency of mechanized cleaning of road and sprinkling of water on roads. Identify road stretches with high dust generation. | All road owning agencies including. Municipal Corporations of NCT of Delhi and NCR towns, Public Works Departments and National Highway Authority of India. |
3. Very Poor
- PM 2.5 levels are between 121-250 μg/cu.m Or
- PM 10 levels are between 351-430 μg/cu.m
| Action to be Taken | Agency Responsible/ Implementing Agency |
| Stop use of diesel generator sets | Chairpersons Delhi Pollution Control Committee, State Pollution Control Boards of Haryana, Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh. |
| Enhance parking fee by 3-4 times | Municipal Commissioner. Municipal Corporations of NCT of Delhi and NCR Towns |
| Increase bus and metro services by augmenting contract buses and increasing frequency of service. | Principal Secretary, Department of Transport of NCT of Delhi. Delhi Integrated Multi-modal Transit System Ltd (DIMTS). DMRC. State Transport Corporations in NCR Towns |
| Stop use of coal/ firewood in hotels and open eateries | Municipal Corporations of NCT of Delhi and NCR Towns |
| Residential Welfare Associations and individual house owners to provide electric heaters during winter to security staff to avoid open burning by them. | Resident Welfare Associations |
| Alert in newspapers/TV/radio to advise people with respiratory and cardiac patients to avoid polluted areas and restrict outdoor movement. | Chairpersons, DPCC and State Pollution Control Boards of Haryana, Rajasthan, and Uttar Pradesh. |
4. Moderate to Poor
- PM 2.5 levels are between 61-120 μg/cu.m Or
- PM 10 levels are between 101-350 μg/cu.m
| Action to be Taken | Agency Responsible/ Implementing Agency |
| Stringently enforce/stop garbage burning in landfills and other places and impose heavy fines on person responsible | Municipal Commissioner. Municipal corporations of Delhi and NCR Towns |
| Close/ stringently enforce all pollution control regulations in brick kilns andindustries | Chairpersons, DPCC and State Pollution Control Boards of Haryana, Rajasthan, and Uttar Pradesh |
| Stringently enforce pollution control in thermal power plants through PCB monitoring | Plant in-charge of power plants in NCR, and Delhi Pollution Control Committee and State Pollution Control Boards of Haryana, Rajasthan and Uttar Pradesh |
| Do periodic mechanized sweeping on roads with heavy traffic and water sprinkling also on unpaved roads every two days | Municipal Commissioner, Municipal Corporations of NCT of Delhi and NCR towns. Commissioners, Traffic Police of Delhi and NCR towns to identify roads with heavy traffic and provide information to respective Municipal Commissioners. Chief Engineers of officers in charge of CPWD, PWD of Delhi and NCR towns to identify unpaved roads with heavy traffic and provide information to respective Municipal Commissioners. |
| Strict vigilance and no tolerance for visible emissions – stop plying of visibly polluting vehicles by impounding or heavy fine. | Commissioner or Officer in Charge, Transport Department and Traffic Police of NCT Delhi and NCR towns |
| Strict vigilance and enforcement of PUC norms | Commissioner or Officer in Charge, Transport Department and Traffic Police of NCT Delhi and NCR town |
| Stringently enforce rules for dust control in construction activities and close non-compliant sites | Commissioner or Officers in charge of Police Departments of Delhi and NCR towns |
| Deploy traffic police for smooth traffic flow at identified vulnerable areas | Commissioners Traffic Police of Delhi and NCR Towns |
| Strictly enforce Supreme Court order on diversion of non-destined truck traffic and ensure only trucks registered after 2005 are allowed entry into Delhi | Municipal Corporations of NCT of Delhi and NCR towns Traffic Police of NCT of Delhi and NCR towns |
| Strictly enforce Supreme Court ban on firecrackers | Chief Controller of Explosives Petroleum and Explosive Safety Organizations (PESO). Commissioner of Officer in charge of licensing in the police departments of Delhi and NCR |
| Ensure fly ash ponds* are watered every alternate day during summer months (March – May). | Plant in charge of Power Plants in Delhi and NCR towns |
| Information dissemination Social media, mobile Apps should be used to inform people about the pollution levels, contact details of control room, enable them to report polluting activities/sources to the concerned authorities, and actions that will be taken by government based on the level of pollution | Chairpersons, DPCC and State Pollution Control Boards of Haryana, Rajasthan, and Uttar Prades |
[cite]




5 thoughts on “AQI Based Graded Response Action Plan for Delhi Explained”